1. Install WordPress
Check your host documentation for instructions on installing WordPress. You can also contact their support department.
2. Log into your new WordPress Account
Now that you’ve installed WordPress, it’s time to login to access the dashboard.
1. Enter your ADMIN URL in the address field of your browser.
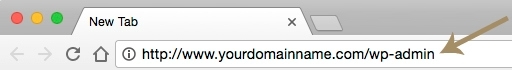
2. Enter your USERNAME and PASSWORD. Click “Log In.”
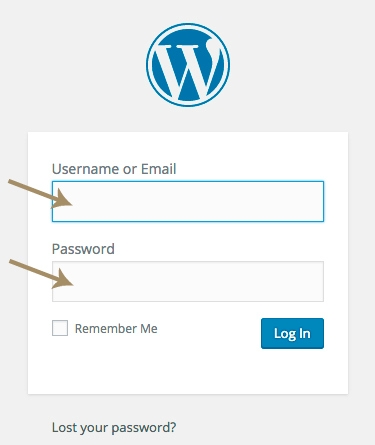
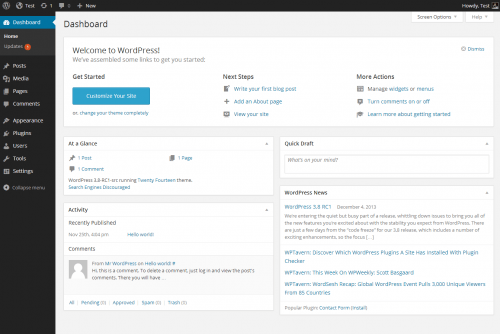
3. Voila! Here’s your new WordPress dashboard! Go ahead … take a look around. Don’t worry, you won’t break anything!
You’ll notice in the “At A Glance” box that WordPress has provided a sample post, a sample comment on that post, and a sample page. You’ll also see a note that WordPress is running a pre-installed theme. This is provided to give you an idea of the basic functionality of WordPress.
Four things to do after WordPress is installed
1. REMOVE ANY UNNECESSARY PLUGINS
A plugin is a piece of software that can be added to a WordPress website to extend the functionality of your site. When you first install WordPress you will have plugins that are automatically installed by your hosting provider. You can delete all the plugins that come installed automatically outside of the host specific plugins. For example, Bluehost will install a Bluehost plugin or Siteground will install the SG Optimizer plugin and you’ll leave that one installed.
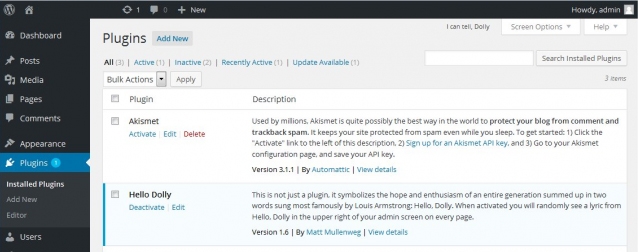
How to uninstall a plugin
- Navigate to the left side of the dashboard, hover over Appearance>Plugins.
If the plugin you want to remove is activated, click on “Deactivate.” - Select all the plugins you want to delete by clicking in the box next to the plugin name.
- In the drop down field titled “Bulk Actions,” select “Delete” and click Apply. Note: You can only delete plugins that are not active.
- It will bring up a screen asking you to verify that you want to delete these plugins – click “yes.”
Plugins are fantastic for adding different abilities to your site, but too many plugins can cause issues and conflicts between other plugins. Going forward, you want to make sure that you only have ACTIVE plugins installed that you absolutely need and use on a daily basis for your website.
2. SELECT YOUR PERMALINK STRUCTURE
The next step is to change the permalink structure. The permalink is what identifies how the URLs coming from the site are saved and used.
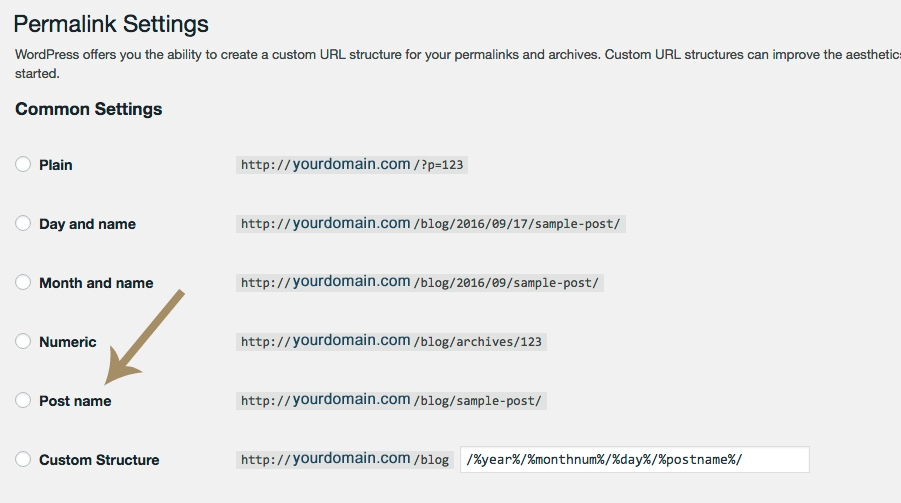
Navigate to the left side of the dashboard, hover over SETTINGS and click on PERMALINK.
When you first install WordPress the permalink structure uses post and page ID’s and it will looks something like this:
http://yourdomain.com/?p=123
This number is not serving any purpose and is disabling the ability for proper keywords to be used for SEO purposes. By changing the permalink, your post and page title content will appear in the URL so that these words can be seen and used for SEO.
We recommend the “Post Name” option. You can choose any of those options but I would recommend NOT using a date in your URL structure for several reasons:
- This date will always be in your URL structure, therefore for SEO purposes, this information is dated and will eventually be old content. To keep your posts timeless to search engines, it’s best to leave the date off.
- If you ever want to repost a post you can simply change the date and repost it without breaking the old permalink. So what’s wrong with duplicating the post and reposting? This is seen to search engines as duplicate content and therefore results in penalties.
3. UPDATE YOUR GENERAL SETTINGS
Navigate to the left side of the dashboard, and go to Settings>General.
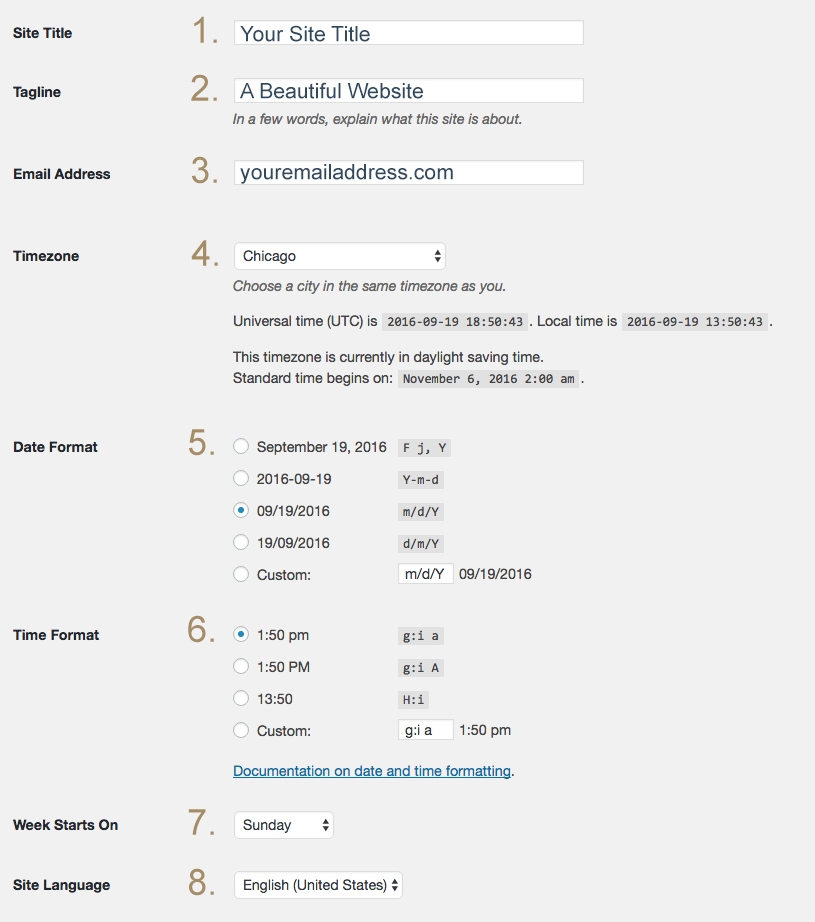
1. Site Title – Google and other search engines use this information when your site is displayed, as shown in the example below. Google typically displays the first 50-60 characters of a title tag, or as many characters as will fit into a 512-pixel display. If you keep your titles under 55 characters, you can expect at least 95% of your titles to display.
2. Tagline – Using a few words, explain what your site is about. This information is also displayed by search engines. Keep your tagline to about 55 characters as well.
3. Email Address – Make sure you have entered a valid email address. This address is used by WordPress to send messages regarding the administration and maintenance of your WordPress site. As an example, if you allow new users to register as a member of your site, those notifications will be sent through e-mail to this address. Also, if comments must be approved, this e-mail address will receive notification that the comment is being held for moderation. Please note this is different than the address you supplied for the admin user account; the admin account e-mail address is sent an e-mail only when someone submits a comment to a post by admin. The address you enter here will never be displayed on the site.
4. Timezone – Select the correct timezone for your website.
5. Date Format – Choose the desired date format.
6. Time Format – Choose the desired time format.
7. Week Starts On – Choose the day you want the week to start on.
8. Site Language – This is the WordPress Dashboard language.
4. Getting to know WordPress
If you’re just getting started with WordPress we recommend the free Understanding WordPress course from iMark Interactive. Since your site is already setup, you can scroll down to the section titled “The WordPress Dashboard” and start there.

